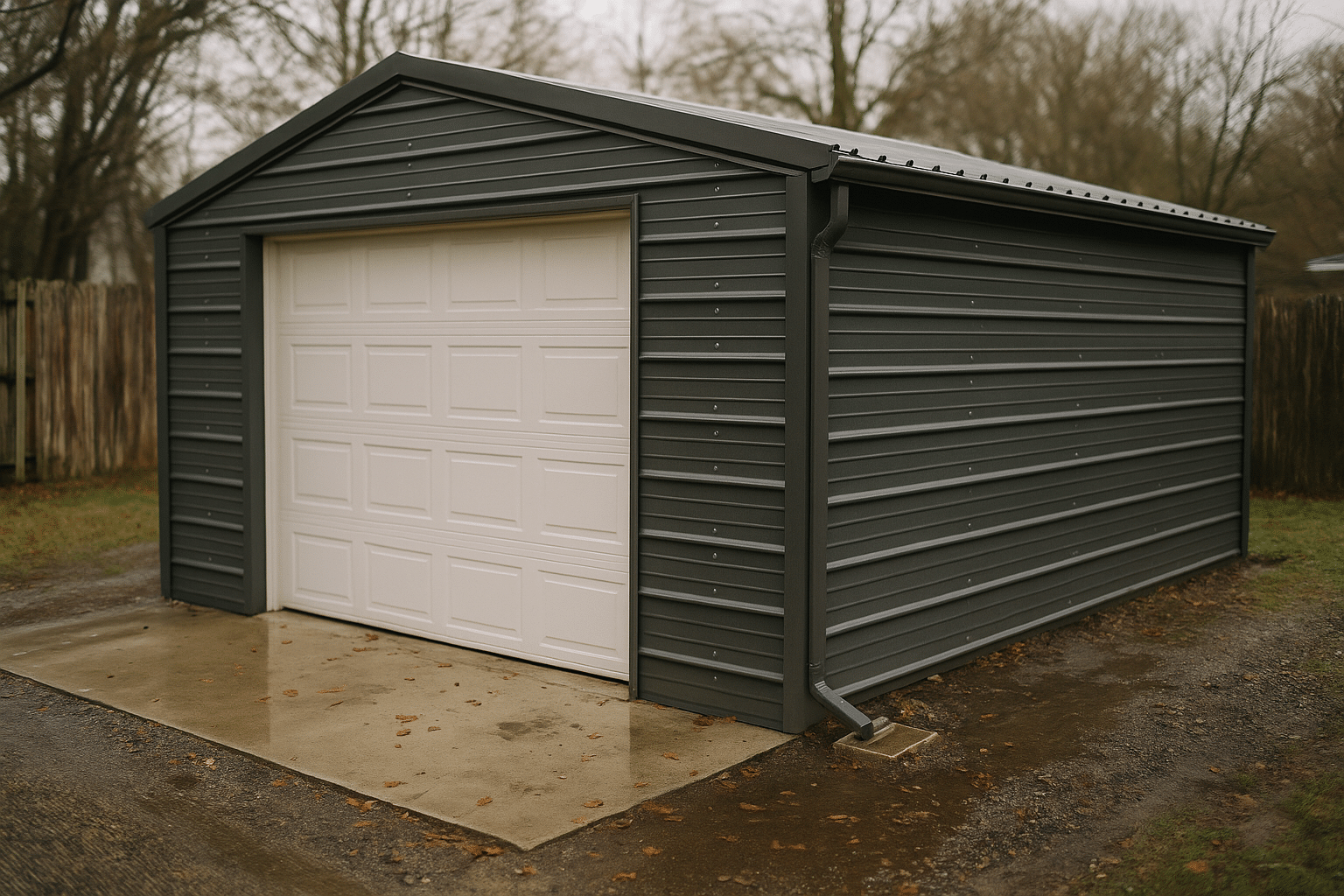
Prefabricated Garage: Planning, Cost Considerations, and Installation Tips
Outline
Here is the roadmap for this guide, so you can skim first and dive deep where it matters:
– Planning and siting: determine purpose, size, layout, and code constraints.
– Cost breakdown: kit pricing, foundation, delivery, permits, and operating costs.
– Materials and durability: steel, wood, and engineered panels compared by climate and maintenance.
– Installation and timeline: site prep steps, delivery day, assembly sequence, and inspections.
– Maintenance, upgrades, and conclusion: caring for the structure, value strategies, and next steps.
Planning: Purpose, Size, and Siting Essentials
A clear plan saves time, money, and headaches. Start with purpose: storage for a compact car is different from housing a tall SUV, a workshop, or a lawn equipment bay. Typical footprints include 12×20 feet for a single vehicle, 20×24 feet for a two-car layout, and deeper bays (24–28 feet) if you need a workbench or room to open tailgates. Height matters, too—consider door clearances for roof racks, the arc of overhead doors, and whether you might add a car lift later. As you map the layout, align doors with the existing driveway and allow turning radius for comfortable ingress and egress. If snow is common, orient the roof pitch to shed drifts away from walk paths; in sunny regions, think about a south- or west-facing roof if future solar panels are on your mind. Throughout this early phase, remember that Prefabricated Garages deliver speed, but codes and logistics still shape the result. Most jurisdictions regulate setbacks from property lines, maximum height, and stormwater runoff. If you live in a community with a design review board, check rules for cladding colors, trim, and roofing style. Site constraints drive details: sloped lots may need a stepped foundation or retaining solution; clay soils often require better drainage and compaction; and high-wind zones may demand specific anchoring hardware. Bring utilities into the conversation early, even if you only need lighting and a few outlets. It is more efficient to trench conduit and plan breaker capacity now than to retrofit later. A quick pre-build checklist helps clarify priorities:
– Define primary use: parking, storage, workshop, or mixed.
– Confirm vehicle dimensions, door style, and headroom targets.
– Verify zoning, setbacks, easements, and HOA design rules.
– Evaluate drainage, driveway alignment, and snow or sun exposure.
– Plan utility stubs: electrical, lighting, and optional data line.
Solid planning shapes a garage that feels effortless to use the day the keys turn.
Cost Considerations: From Kit to Keys
Budgets are clearer when you break them into line items. Start with the structure: basic single-car kits often begin around $3,500–$8,000, mid-range wood or steel options commonly fall between $8,000–$18,000, and larger or upgraded two-car configurations can reach $20,000–$30,000 or more, depending on finishes and door type. Foundations add a significant percentage: a reinforced concrete slab typically ranges $4–$9 per square foot, with thicker edges or frost footings pushing higher in cold climates. Site preparation—grading, gravel base, and minor excavation—often runs $1–$5 per square foot, influenced by soil conditions and access. Delivery fees vary by distance and size but commonly land between $300 and $1,500. Permits and inspections can total $50–$1,000 depending on local rules. If you hire assembly help, labor may add $1,500–$6,000 for a single-bay and more for multi-bay layouts, particularly when upgrades like windows, skylights, or complex trim are involved. Electrical rough-in often ranges $800–$2,500, but longer trench runs or subpanel work can increase costs. Just as important, carry a contingency—10–15% cushions unexpected needs like a deeper slab edge, a revised door opening, or additional drainage. Because Prefabricated Garages compress schedules, you may save on labor compared with fully custom builds, but customization still affects price. To keep spending in check:
– Choose standard sizes and door openings to avoid special-order fees.
– Limit unique colors or complex trim profiles that add labor time.
– Schedule delivery during a dry spell to reduce site delays and rework.
– Coordinate inspections early to prevent idle days between steps.
Operating costs deserve attention, too. Insulation ups the initial outlay but usually trims heating loads in cold zones and fights condensation wherever temperature swings are common. LED fixtures and timers cut electricity use, while a simple air-seal pass around doors and windows improves comfort. Property value impacts vary by market, but garage additions frequently return a meaningful share of their cost—often cited in the 60–80% range—while delivering day-to-day utility from secure storage and weather protection.
Materials and Durability: Matching the Build to Your Climate
Materials dictate longevity, upkeep, and how the building behaves through the seasons. Steel panel systems are popular for their strength-to-weight ratio and quick assembly; they resist pests and can be engineered for high snow or wind loads. In coastal or high-salt areas, look for galvanization and well-detailed trim to shield cut edges, and plan routine rinsing to minimize corrosion. Wood-framed kits offer familiar aesthetics and flexibility for shelving or interior finishing; they insulate easily, accept a wide variety of sidings, and are simple to repair, though they require periodic sealing or repainting. Engineered composite panels offer stability against warping and can deliver clean lines that blend with contemporary homes. Across all options, fasteners, flashing, and sealants do quiet but essential work—quality hardware reduces loosening, and correctly lapped trim guards against wind-driven rain. Insulation is more than comfort; it controls condensation, protects stored items, and reduces energy costs. In temperate regions, a modest R-13/R-19 wall and R-30 ceiling can be adequate; in colder zones, higher R-values or continuous exterior insulation may be prudent. Ventilation matters as much as insulation: ridge and soffit vents promote airflow, while a small through-wall fan clears fumes from projects. Prefabricated Garages thrive when matched to their environment—choose coatings rated for UV exposure in sunny climates, and consider snow-shedding roof profiles where winters are heavy. A maintenance mindset preserves value:
– Wash exterior panels once or twice a year; remove salt and debris.
– Touch up paint or protective coatings at early signs of wear.
– Clear gutters and confirm downspouts discharge away from the slab.
– Inspect door seals and weatherstripping before winter and summer.
– Tighten exposed fasteners and check anchors after major storms.
If you plan to heat or cool the space, specify a continuous air barrier and proper vapor retarder location for your climate zone to avoid trapped moisture.
Installation and Timeline: What to Expect, Step by Step
A smooth install begins with logistics. Before delivery, confirm the truck route, measure gate widths, and clear the staging area so materials can be set close to the foundation. Foundations differ by region and use: floating slabs work in mild climates, while frost-protected shallow foundations or perimeter footings are common in colder zones. Allow concrete to cure per local practice before loading; even with rapid-setting mixes, plan days—not hours—before assembly. Many kits arrive pre-cut and labeled, which accelerates framing and panel attachment. Single-bay units often assemble in one to three days with an experienced crew; two-car layouts commonly take three to five days, especially if windows, skylights, or interior sheathing are included. If weather turns, protect exposed components and pause rather than push ahead into wind or rain. While the appeal of Prefabricated Garages is speed, don’t skip the details that deliver longevity. Flash door and window openings, bed sill plates on a proper gasket, and verify square and plumb at each stage to prevent cumulative errors. Keep inspections in sequence: footing or slab approval, rough frame, and final sign-off, as required. A delivery-day quick list helps reduce surprises:
– Confirm permit card and inspection schedule are on-site.
– Stage tools, fasteners, sealants, and safety gear in one spot.
– Set tarps to cover materials if a shower rolls through.
– Verify door and window sizes against openings before fastening.
– Photograph anchor and flashing details for your records.
Post-assembly, finish edges, caulk joints, and touch up coatings. If you plan electrical, rough-in before interior wall finishes. Finally, check door balance and smooth travel; proper adjustment prevents early wear and air leaks.
Maintenance, Upgrades, and Conclusion: Getting Long-Term Value
Once the structure is standing, the real return comes from daily ease of use and low-hassle upkeep. Sweep or hose the slab regularly to keep grit from grinding into coatings; a light degreaser lifts oil spots before they stain deeply. If you live where freeze-thaw cycles are pronounced, seal the slab edges to reduce spalling. Doors appreciate attention: lubricate rollers and hinges twice a year, check spring balance, and replace worn seals so wind and dust stay out. Exterior care is simple but important—wash siding, inspect fasteners, and touch up paint or protective finishes where you see scuffs or UV fade. Thoughtful upgrades extend utility. Add insulation and a modest heater if you work year-round; include a dehumidifier in humid climates to protect tools. Run a dedicated circuit for high-draw equipment and keep general lighting on separate switches so you can brighten work zones without wasting energy. Pegboards, wall-mounted shelves, and ceiling storage keep floors clear and airflow steady. For floors, consider a breathable coating or mats that won’t trap moisture beneath. Water management matters: clean gutters before storm seasons, extend downspouts, and regrade if puddles form against the slab. These habits help Prefabricated Garages stay clean, dry, and ready for whatever you park or build inside. When you think about resale and appraisal, curb appeal counts: match trim colors to the house, add modest landscaping, and ensure the driveway meets the threshold smoothly. Many homeowners report that a well-placed, tidy garage boosts perceived property value and buyer confidence. If you’re weighing next steps, sketch a simple roadmap:
– Year 1: finalize storage systems and dial in lighting and outlets.
– Year 2: add insulation or air sealing if comfort is lacking.
– Year 3: refresh exterior coatings and reassess drainage patterns.
– Anytime: tighten hardware, clean door tracks, and verify anchors.
In short, aim for a space that is organized, weather-resilient, and easy to maintain. Those traits deliver daily convenience now and make selling easier later, transforming a straightforward project into a durable, low-stress asset.